In the topic of Static Electricity, charging by induction often presents a challenge for students. The process involves several invisible steps — the movement of electrons, the effect of grounding, and the lasting net charge after removing the influencing object. To bridge this gap between theory and understanding, I have created this interactive simulation to help students visualise the interactions and changes. Students can be asked to predict what will happen using various button sequences to help challenge students’ preconceptions about electric charge and behaviour during induction.
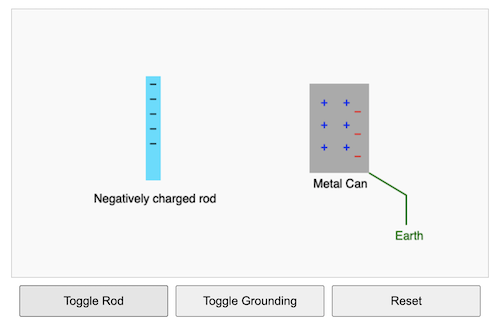
Refer to the scenario above. What will happen next if we:
a) Remove the earth wire before removing the rod, or
b) Remove the rod before removing the earth wire?
