[spoiler title=”Gravitational Field” open=”yes”]
- Newton’s Law of Gravitation states that the gravitational force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation,
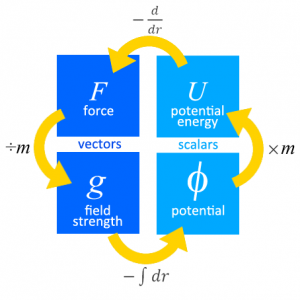
i.e. $$F_G=\dfrac{Gm_1m_2}{r^2}$$ where G is the gravitational constant 6.67 $$\times$$ 10-11 N kg-2m2, m1 and m2 are the masses and r is the distance between them. - Gravitational field strength at a point is defined as the gravitational force acting per unit mass placed at that point,
i.e. $$g=\dfrac{F_G}{m_2}=\dfrac{Gm_1}{r^2}$$ where m1 is the mass of the source of the field. - Gravitational potential energy at a point is defined as the work done by an external agent in bringing a body from infinity to that point (without any change in kinetic energy),
i.e. $$U=-\dfrac{Gm_1m_2}{r}$$ - Gravitational potential at a point is defined as the work done per unit mass by an external agent in bringing a body from infinity to that point (without any change in kinetic energy),
i.e. $$V=-\dfrac{Gm_1}{r}$$
[/spoiler]
[spoiler title=”Interplanetary Travel”]
- Escape speed is the minimum speed at which a body of mass m can be projected from the surface of a planet of mass M so that it reaches an infinite distance from the planet.
- By conservation of energy,
initial total energy = final total energy
$$U_i+E_{k_i}=U_f+E_{k_f}\\-\dfrac{GMm}{r}+\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2=0+0$$
$$v=\sqrt{2GM}$$
[/spoiler]
[spoiler title=”Satellite Motion”]
- For an object with mass m in orbit,
Gravitational Force = Centripetal Force
$$F_G=F_C\\\dfrac{GMm}{r^2}=mr\omega^2\\\dfrac{GM}{r^2}=r(\dfrac{2\pi}{T})^2\\\text{period, }T=2\pi\sqrt{\dfrac{r^3}{GM}}$$ - $$F_G=F_C\\\dfrac{GMm}{r^2}=\dfrac{mv^2}{r}\\\text{orbital speed, }v=\sqrt{\dfrac{GM}{r}}$$
- kinetic energy, $$E_k=\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2=\dfrac{GMm}{2r}$$
- total energy, $$E_T=E_k+U=\dfrac{GMm}{2r}-\dfrac{GMm}{r}=-\dfrac{GMm}{2r}$$
[/spoiler]
[spoiler title=”Geostationary Satellites”]
- A geostationary satellite (one that is always above the same point on the Earth) has to be in an equatorial orbit, i.e. the orbit is in the same plane as that of the equator, so that
- the centripetal force points towards the centre of the plane, and
- it moves in the same direction of rotation as the Earth, i.e. from west to east.
- It has a period of 24 h, i.e. same period as the Earth.
- It orbits with a fixed radius of 4.20 $$\times$$ 107 m from the Earth’s centre.
[/spoiler]
Have you heard of the MEGA theory? – Animated Granular Space Model (Modèle d’Espace Granulaire Animé) This theory would find its place upstream of Relativity and Quantum Mechanics and seems to be able to unify them. And it is, oddly enough, rather simple.
It explains gravitation, and disputes the existence of dark matter.
It justifies the cosmic radiation spectrum on the basis of a non-probability-based interpretation of Planck’s law.
It offers a new interpretation of E=mc².
It affirms that everything said there is verifiable.
How relevant is it? I would like to discuss that.
Location: http://www.kbj-modele.fr